Draw the electron configuration for a neutral atom of nickel. – Drawing the electron configuration for a neutral atom of nickel is a fundamental step in understanding its chemical properties and behavior. The electron configuration provides insights into the arrangement of electrons within the atom’s orbitals, which in turn influences its reactivity and bonding characteristics.
This article delves into the electron configuration of nickel, exploring its significance, Aufbau principle, valence electrons, periodic trends, and applications. By understanding these aspects, we gain a deeper appreciation of nickel’s unique position in the periodic table and its diverse uses in various industries.
Electron Configuration of Neutral Nickel: Draw The Electron Configuration For A Neutral Atom Of Nickel.

Electron configuration describes the distribution of electrons in an atom’s orbitals. It plays a crucial role in determining an element’s chemical properties.
The electron configuration of a neutral nickel atom is:
s22s 22p 63s 23p 63d 84s 2
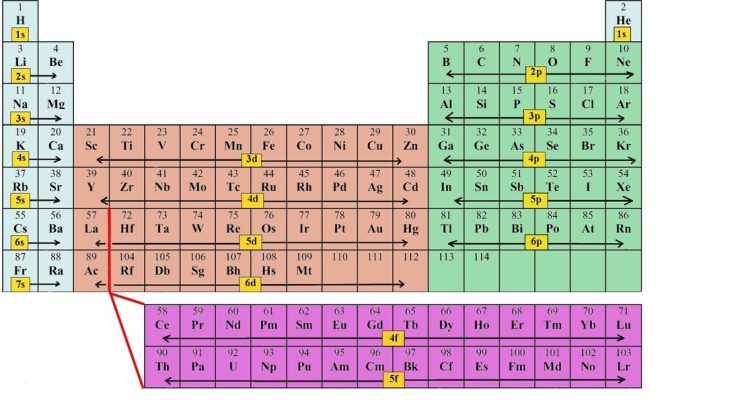
The Aufbau principle states that electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy levels. Nickel’s electron configuration follows this principle, with electrons occupying the 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 3d, and 4s orbitals in that order.
Valence Electrons and Chemical Properties, Draw the electron configuration for a neutral atom of nickel.
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom. Nickel has two valence electrons in the 4s orbital.
Valence electrons strongly influence an element’s chemical properties. Nickel’s two valence electrons allow it to form two bonds with other atoms, making it a transition metal.
For example, nickel reacts with chlorine to form nickel(II) chloride (NiCl 2), in which nickel shares its two valence electrons with two chlorine atoms.
Periodic Trends and Electron Configuration
Nickel is in Group 10 of the periodic table, along with palladium and platinum. These elements share a similar electron configuration in their outermost d orbitals (d 8).
Across a period, the number of valence electrons increases. This affects the elements’ reactivity and other properties.
Nickel’s electron configuration contributes to its unique position in the periodic table. Its d 8configuration gives it stability and makes it resistant to oxidation.
Applications of Nickel
Nickel has numerous applications due to its strength, corrosion resistance, and magnetic properties.
Nickel is used in:
- Stainless steel
- Coins
- Batteries
- Catalysts
Nickel-based alloys are also used in high-temperature applications, such as jet engines and rocket parts.
Key Questions Answered
What is the electron configuration of a neutral atom of nickel?
The electron configuration of a neutral atom of nickel is 1s 22s 22p 63s 23p 63d 84s 2.
How many valence electrons does nickel have?
Nickel has 10 valence electrons.
What is the Aufbau principle?
The Aufbau principle states that electrons fill orbitals in the order of increasing energy levels.