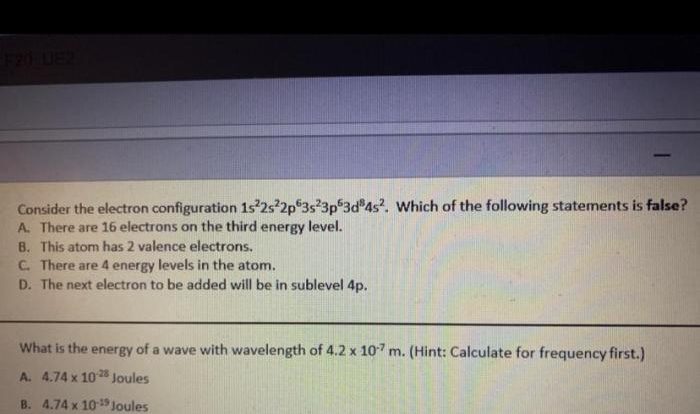
The orbital diagram for a ground-state nitrogen atom is – The orbital diagram of a ground-state nitrogen atom is a visual representation of the arrangement and energy levels of its electrons. Understanding this diagram provides crucial insights into the chemical properties and behavior of nitrogen, an essential element in biological processes and industrial applications.
Nitrogen’s ground-state electron configuration, 1s 22s 22p 3, dictates the distribution of its electrons within specific orbitals, each characterized by its unique shape and energy level.
Introduction

An orbital diagram is a visual representation of the arrangement of electrons in an atom. It provides insights into the energy levels and shapes of the atomic orbitals, which are the regions where electrons are most likely to be found.
By analyzing the orbital diagram of a ground-state nitrogen atom, we can understand its electron configuration, chemical properties, and reactivity.
Understanding the Ground-State Nitrogen Atom

In its ground state, nitrogen has an electron configuration of 1s 22s 22p 3. This means that it has two electrons in the 1s orbital, two electrons in the 2s orbital, and three electrons in the 2p orbitals.
Atomic orbitals are three-dimensional regions around the nucleus where electrons are most likely to be found. They have specific shapes and energy levels, which are determined by the quantum numbers of the electrons.
Orbital Diagram of Ground-State Nitrogen Atom

The orbital diagram of ground-state nitrogen atom is as follows:
| Orbital | Energy Level | Sublevel | Electron Spin |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1s | 1 | s | ↑↓ |
| 2s | 2 | s | ↑↓ |
| 2px | 2 | p | ↑ |
| 2py | 2 | p | ↑ |
| 2pz | 2 | p | ↑ |
Properties of the Nitrogen Atom
The orbital diagram of nitrogen provides valuable insights into its chemical properties. The presence of three unpaired electrons in the 2p orbitals indicates that nitrogen is a highly reactive element. It readily forms covalent bonds with other atoms to achieve a stable electron configuration.
Comparison with Other Nitrogen Species: The Orbital Diagram For A Ground-state Nitrogen Atom Is

Excited-state nitrogen atoms have different electron configurations and orbital diagrams compared to the ground state. For example, in the first excited state, one of the 2p electrons is promoted to the 3s orbital. This changes the electron configuration to 1s 22s 22p 23s 1and alters the chemical properties of nitrogen.
Applications of Orbital Diagrams
Orbital diagrams are widely used in chemistry to understand various aspects of atomic and molecular behavior. They are essential for:
- Predicting the bonding behavior and reactivity of elements
- Explaining molecular structure and geometry
- Interpreting spectroscopic data
FAQs
What is the significance of the orbital diagram for a ground-state nitrogen atom?
It provides a detailed representation of the electron distribution, energy levels, and orbital shapes, which are essential for understanding nitrogen’s chemical behavior.
How does the electron configuration of nitrogen affect its properties?
The specific arrangement of electrons in the 1s, 2s, and 2p orbitals influences nitrogen’s bonding capabilities, reactivity, and magnetic properties.
What are the practical applications of orbital diagrams?
Orbital diagrams aid in predicting molecular structures, explaining chemical bonding, interpreting spectroscopic data, and designing new materials with tailored properties.