Unit gas laws ideal gas law wksh 4 answer key – Delving into the fascinating realm of unit gas laws and the ideal gas law, this comprehensive guide provides a thorough understanding of the behavior of gases. Embark on a journey through Boyle’s law, Charles’s law, and Gay-Lussac’s law, gaining insights into the relationships between pressure, volume, and temperature.
Discover the combined gas law and the ideal gas law, unlocking the secrets of gas behavior under varying conditions. This exploration unravels the applications of gas laws in diverse fields, showcasing their significance in chemistry, physics, and engineering.
Introduction to Unit Gas Laws
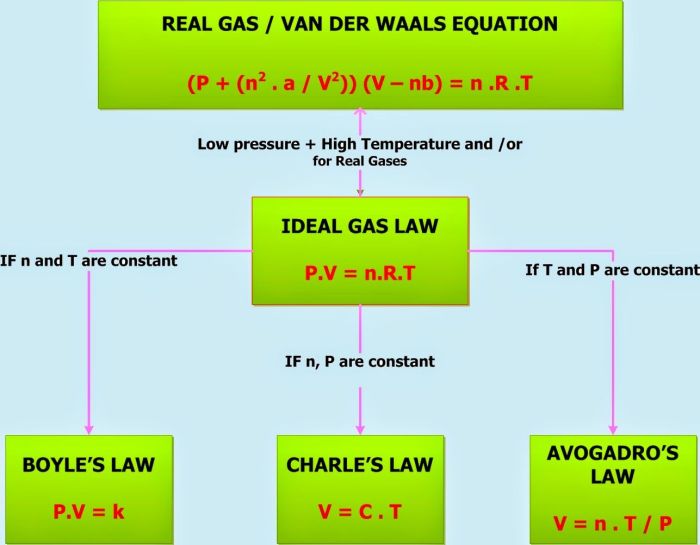
Unit gas laws are a set of equations that describe the behavior of gases under various conditions. These laws are essential for understanding the behavior of gases in a wide range of applications, from chemistry to engineering.
The three main unit gas laws are Boyle’s law, Charles’s law, and Gay-Lussac’s law. Boyle’s law describes the relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas at constant temperature. Charles’s law describes the relationship between the volume and temperature of a gas at constant pressure.
Gay-Lussac’s law describes the relationship between the pressure and temperature of a gas at constant volume.
Boyle’s Law, Unit gas laws ideal gas law wksh 4 answer key
Boyle’s law states that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume at constant temperature. This means that as the volume of a gas increases, its pressure decreases, and vice versa.
The mathematical formula for Boyle’s law is P₁V₁ = P₂V₂.
Boyle’s law can be used to solve a variety of problems involving gases. For example, it can be used to determine the pressure of a gas in a container of known volume, or to determine the volume of a gas at a known pressure.
Charles’s Law
Charles’s law states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature at constant pressure. This means that as the temperature of a gas increases, its volume increases, and vice versa.
The mathematical formula for Charles’s law is V₁/T₁ = V₂/T₂.
Charles’s law can be used to solve a variety of problems involving gases. For example, it can be used to determine the volume of a gas at a known temperature, or to determine the temperature of a gas at a known volume.
Gay-Lussac’s Law
Gay-Lussac’s law states that the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature at constant volume. This means that as the temperature of a gas increases, its pressure increases, and vice versa.
The mathematical formula for Gay-Lussac’s law is P₁/T₁ = P₂/T₂.
Gay-Lussac’s law can be used to solve a variety of problems involving gases. For example, it can be used to determine the pressure of a gas at a known temperature, or to determine the temperature of a gas at a known pressure.
Helpful Answers: Unit Gas Laws Ideal Gas Law Wksh 4 Answer Key
What is the significance of unit gas laws?
Unit gas laws provide a fundamental understanding of how gases behave under varying conditions, enabling scientists and engineers to predict and manipulate gas behavior in practical applications.
How is Boyle’s law applied in real-world scenarios?
Boyle’s law finds applications in scuba diving, where understanding the relationship between pressure and volume is crucial for safe diving practices. It also plays a role in the design of pressure cookers and aerosol cans.
What is the difference between Charles’s law and Gay-Lussac’s law?
Charles’s law focuses on the relationship between volume and temperature, while Gay-Lussac’s law examines the relationship between pressure and temperature. Both laws are essential for understanding gas behavior under varying temperature conditions.