Coronary artery disease hesi case study – The HESI case study on coronary artery disease (CAD) delves into the intricacies of this prevalent cardiovascular condition, providing a comprehensive overview of its pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and management. This study aims to equip healthcare professionals with the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively care for patients with CAD, empowering them to improve patient outcomes and enhance quality of life.
As we delve into the complexities of CAD, we will explore the underlying mechanisms leading to its development, the various diagnostic tests employed to identify it, and the range of treatment options available. Additionally, we will emphasize the crucial role of nurses in patient care, highlighting the principles of patient education, symptom management, and lifestyle modifications.
Definition and Overview of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a condition in which the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked. This can lead to a heart attack, which occurs when the blood supply to the heart is completely blocked.
Causes and Risk Factors, Coronary artery disease hesi case study
CAD is caused by the buildup of plaque in the arteries. Plaque is made up of cholesterol, fat, calcium, and other substances. Over time, plaque can build up and narrow the arteries, making it difficult for blood to flow through them.
The risk factors for CAD include:
- High cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Family history of CAD
Prevalence and Impact
CAD is the leading cause of death in the United States. In 2020, an estimated 697,000 Americans died from CAD. CAD is also a major cause of disability, and it can lead to a number of serious health problems, including heart failure, stroke, and kidney failure.
Pathophysiology of CAD
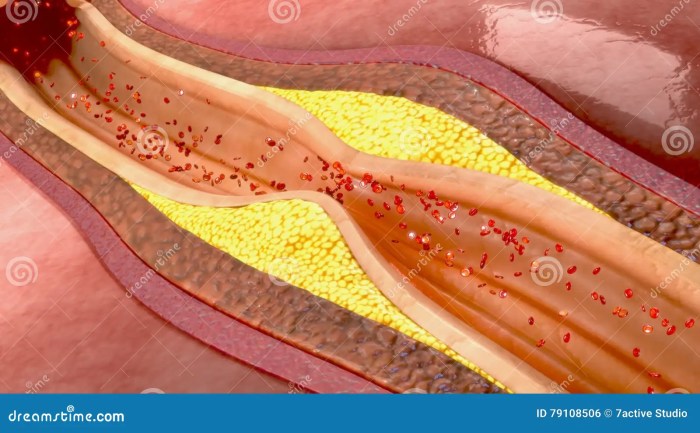
CAD is a complex disease that involves a number of different processes. The first step in the development of CAD is the accumulation of cholesterol in the arteries. This cholesterol can come from the diet or it can be produced by the body.
Once cholesterol has accumulated in the arteries, it can start to form plaque.
Role of Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is the process by which plaque builds up in the arteries. Atherosclerosis begins with the formation of fatty streaks, which are small, yellow deposits of cholesterol and other substances. Over time, fatty streaks can grow and become more complex, forming atherosclerotic plaques.
Composition of Atherosclerotic Plaques
Atherosclerotic plaques are made up of a number of different substances, including cholesterol, fat, calcium, and fibrous tissue. The composition of a plaque can vary depending on its stage of development. Early plaques are soft and contain a high percentage of cholesterol.
As plaques progress, they become harder and more calcified.
Query Resolution: Coronary Artery Disease Hesi Case Study
What are the common risk factors for coronary artery disease?
Major risk factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, obesity, physical inactivity, and family history of CAD.
What are the typical symptoms of stable angina?
Chest discomfort or pain, typically described as pressure, squeezing, or tightness, that occurs with exertion or stress and is relieved by rest or nitroglycerin.
How is coronary angiography performed?
A thin, flexible tube (catheter) is inserted into an artery in the arm or leg and guided to the heart. Dye is injected through the catheter to visualize the coronary arteries and identify any blockages or narrowing.