The life cycle of stars worksheet – Embark on an illuminating journey through the life cycle of stars with this comprehensive worksheet. From their celestial birth to their ultimate demise, discover the intricate stages that shape the cosmos and unravel the mysteries of stellar evolution.
This worksheet delves into the fascinating processes of star formation, internal structure, classification, and the diverse ways stars meet their end. Explore the impact of stars on life and the search for exoplanets, expanding our understanding of the universe and our place within it.
Stellar Evolution: The Life Cycle Of Stars Worksheet
Stellar evolution refers to the series of changes that stars undergo throughout their lifetimes. It encompasses the processes from the formation of stars to their ultimate fate.The stages of stellar evolution are as follows:
-
-*Protostar
A dense cloud of gas and dust that collapses under its own gravity, forming a protostar.
-*Main Sequence Star
A star that is fusing hydrogen in its core, maintaining a stable balance between gravitational collapse and outward pressure.
-*Red Giant
A star that has exhausted its hydrogen fuel in its core and expanded, becoming cooler and redder.
-*White Dwarf
A remnant of a low-mass star that has shed its outer layers and collapsed into a dense, hot core.
-*Neutron Star
A remnant of a high-mass star that has undergone a supernova explosion and collapsed into an extremely dense core composed of neutrons.
-*Black Hole
A region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape.
| Stage | Mass | Radius | Temperature ||—|—|—|—|| Protostar | Varies | Varies | Varies || Main Sequence Star | Varies | Varies | Varies || Red Giant | Varies | Expanded | Cooler || White Dwarf | Low | Compact | Hot || Neutron Star | High | Compact | Extremely hot || Black Hole | Varies | Singularity | N/A |
Star Formation
Star formation occurs when a cloud of gas and dust, known as a molecular cloud, collapses under its own gravity. As the cloud collapses, it fragments into smaller and smaller clumps, each of which can form a star.The process of star formation involves the following steps:
-
-*Gravitational Collapse
The cloud collapses under its own gravity, forming a protostar.
-*Accretion
Gas and dust from the surrounding cloud continue to fall onto the protostar, increasing its mass.
-*Nuclear Fusion
Once the protostar reaches a sufficient mass, the temperature and pressure in its core become high enough for nuclear fusion to begin.
-*Main Sequence Star
The protostar becomes a main sequence star, fusing hydrogen in its core and emitting light.
Star formation is influenced by several factors, including the density of the molecular cloud, the presence of dust and gas, and the magnetic field of the cloud.
Stellar Structure and Properties
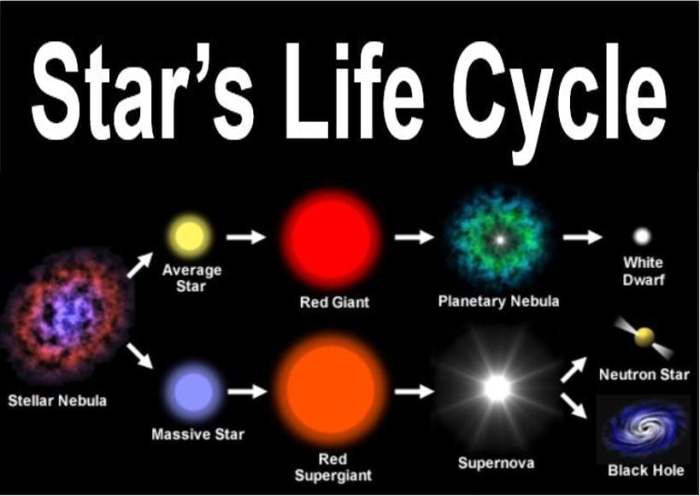
Stars are composed of plasma, a hot, ionized gas. They have a layered structure, with the core at the center, followed by the radiative zone and the convective zone.
-
-*Core
The core is the hottest and densest part of the star, where nuclear fusion occurs.
-*Radiative Zone
The radiative zone is located outside the core and is characterized by the transfer of energy through radiation.
-*Convective Zone
The convective zone is located outside the radiative zone and is characterized by the transfer of energy through convection.
Stellar properties, such as mass, radius, and temperature, affect their evolution. Mass is the most important factor, as it determines the star’s luminosity, lifespan, and ultimate fate. Radius and temperature are also important, as they affect the star’s surface gravity and the rate of nuclear fusion in its core.
Stellar Classification
Stars are classified based on their spectral type and luminosity class. The spectral type is determined by the temperature of the star’s surface, while the luminosity class is determined by the star’s luminosity.The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is a graph that plots the luminosity of stars against their surface temperature.
It is used to classify stars into different spectral types and luminosity classes.| Spectral Type | Surface Temperature (K) ||—|—|| O | >30,000 || B | 10,000
30,000 |
| A | 7,500
10,000 |
| F | 6,000
7,500 |
| G | 5,000
6,000 |
| K | 3,500
5,000 |
| M | <3,500 | | Luminosity Class | Luminosity (Sun = 1) | |---|---| | I | >100 || II | 10
100 |
| III | 1
10 |
| IV | 0.1
1 |
| V | 0.01
0.1 |
Stellar Death

Stars die when they exhaust their nuclear fuel. The way in which a star dies depends on its mass.
-
-*Low-mass stars
Low-mass stars become red giants, then white dwarfs.
-*High-mass stars
High-mass stars undergo supernova explosions, leaving behind neutron stars or black holes.
Stellar death can have a significant impact on the surrounding environment. Supernova explosions can eject heavy elements into space, enriching the interstellar medium. Neutron stars and black holes can also affect their surroundings through their gravitational pull and the emission of radiation.
Impact of Stars on Life
Stars play a crucial role in the existence of life on Earth and beyond.
-
-*Energy
Stars provide the energy that sustains life on Earth through photosynthesis.
-*Elements
Stars create heavy elements through nuclear fusion, which are essential for the formation of planets and life.
-*Habitable Zones
Stars provide habitable zones, which are regions around stars where liquid water can exist on the surface of planets.
The search for exoplanets, planets that orbit stars other than the Sun, is an active area of research. The discovery of exoplanets provides insights into the potential for life beyond Earth.
General Inquiries
What are the main stages of stellar evolution?
The main stages of stellar evolution include the protostar phase, main sequence phase, red giant phase, and white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole phase.
How do stars form?
Stars form within vast clouds of gas and dust called molecular clouds. Gravity causes these clouds to collapse, forming dense cores that eventually ignite nuclear fusion and become stars.
What is the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram?
The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is a graph that plots the luminosity of stars against their surface temperature. It is used to classify stars based on their evolutionary stage and properties.